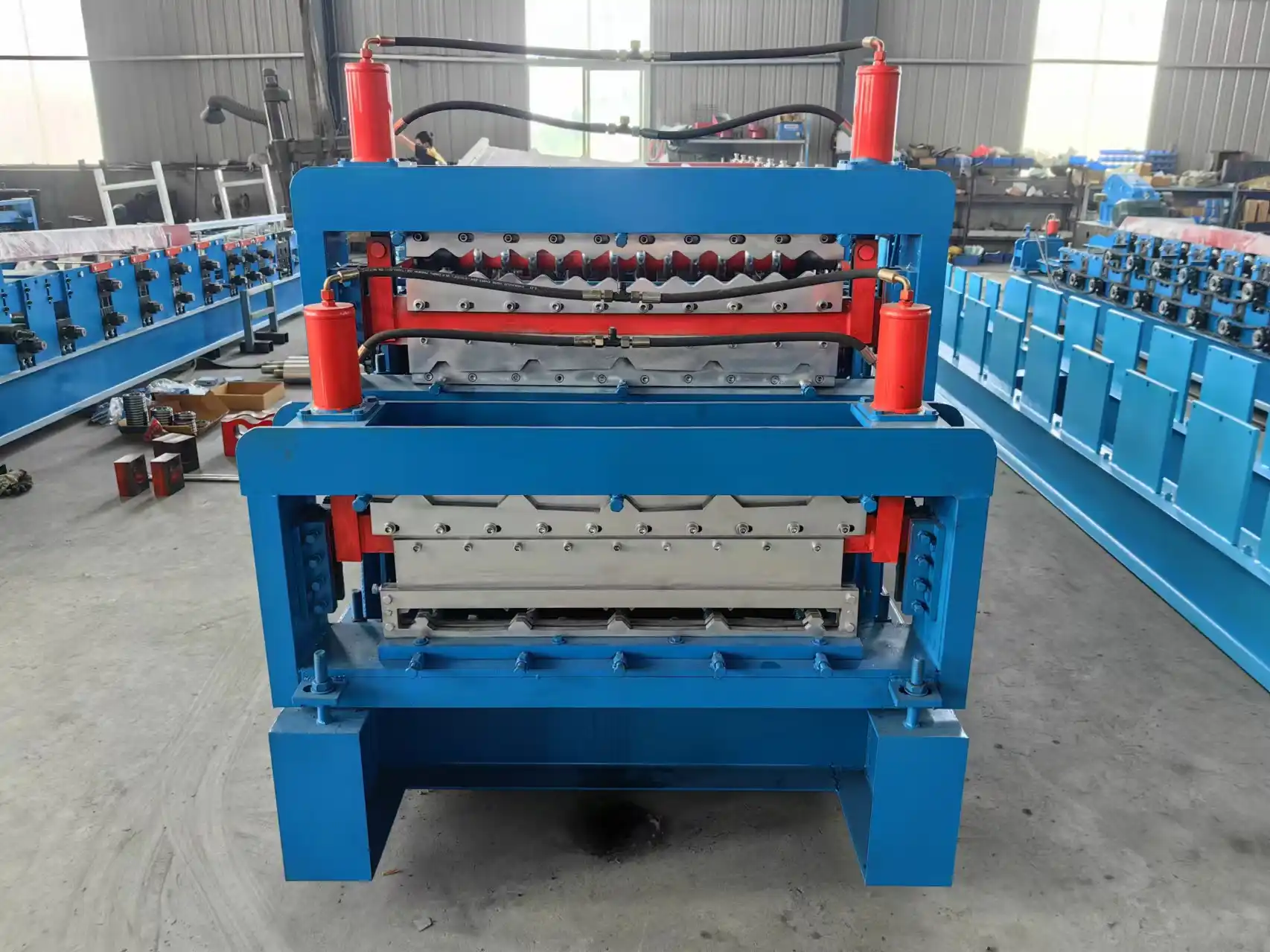
Explore the Range of Hydraulic Bending Machines and Their Uses
Understanding Hydraulic Bending Machines
Basic Principles of Hydraulic Bending
Hydraulic bending machines work by leveraging hydraulic pressure to bend materials, mainly metals. This pressure is produced by a hydraulic cylinder, which compels the material to bend at an exact angle and shape. The hydraulic pump system manages the pressure level and ensures smooth operation to achieve the desired bend. One crucial aspect is maintaining consistent force during the bending process, which guarantees accuracy and repeatability.
XINBO machine is a manufacturer which established in China since 2014. Quality assurance is provided by a team of our machine professional desiginer and producters and workers. New and innovative technology,such as roll forming machine, for the Europe, UK and Canada, as customer’s request and class. And we also have standard class for normal consumption.
Advantages of Using Hydraulic Bending Machines
One of the primary advantages of using hydraulic bending machines is their high level of precision and control. These machines can produce intricate bends that may be impossible with manual methods. Another significant advantage is their versatility; they can be used on a wide range of materials and in various industrial applications. Additionally, Hydraulic Bending Machines are known for their efficiency and speed, which enhances productivity while reducing labor costs. These machines also offer consistent performance, making them a reliable choice for manufacturing needs.
Types of Hydraulic Bending Machines

Manual Hydraulic Bending Machines
Features and Capabilities of Manual Models
Manual hydraulic bending machines are typically compact and user-friendly. They are designed for simpler operations and can handle lower volume tasks efficiently. These machines require manual input to adjust settings and apply hydraulic pressure. Despite their simplicity, they can achieve precise bends and are often equipped with basic control systems to ensure accuracy. Their portability makes them ideal for on-site jobs and small-scale operations.
Common Applications for Manual Machines
Manual hydraulic bending machines are commonly used in tasks that demand less complexity. They are ideal for custom fabrication, repair, and maintenance work where precision is needed but the volume of work is not substantial. These machines are also prevalent in workshops that handle prototype development or small batch production, providing the necessary flexibility to tweak and modify designs as needed.
Semi-Automatic Hydraulic Bending Machines
Characteristics and Benefits of Semi-Automatic Models
Semi-automatic hydraulic bending machines strike a balance between manual control and automation. These models come with more advanced features than manual versions, such as programmable settings and semi-automated operation modes. The semi-automatic mode minimizes the need for operator intervention, thereby boosting consistency and speed. Additionally, they are outfitted with more sophisticated control systems that enhance ease of use and accuracy.
Use Cases for Semi-Automatic Machines
Semi-automatic hydraulic bending machines are well-suited for medium-scale production and projects requiring a higher degree of precision and repeatability. They are frequently used in automotive, construction, and manufacturing industries where there is a need to balance efficiency with versatility. These machines are ideal for producing components with repetitive bends, reducing production time while maintaining high standards of accuracy.
Fully Automatic Hydraulic Bending Machines
Advanced Features of Fully Automatic Models
Fully automatic hydraulic bending machines represent the pinnacle of bending technology. These models come with advanced computerized controls, enabling precise programming of complex bending sequences. They often include features such as automatic material feeding, real-time monitoring, and adaptive control systems. These features ensure optimal performance and minimize the margin of error, making them suitable for high-precision tasks.
Industrial Applications for Fully Automatic Machines
Fully automatic hydraulic bending machines are essential in large-scale production environments where precision and efficiency are paramount. Industries such as aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery rely heavily on these machines for mass production of components. They are ideal for situations where complex bends and high throughput are required, significantly improving production rates while maintaining exceptional quality standards.
Key Components and Functions
Core Components of a Hydraulic Bender
Hydraulic Cylinder and Pump System
The hydraulic cylinder and pump system form the core of any Hydraulic Bending Machine. The pump produces the required pressure, which is then conveyed to the hydraulic cylinder. This cylinder applies the force essential for bending the material. The efficiency and dependability of the machine are significantly influenced by the design and quality of these components. Hydraulic cylinders need to be durable and able to endure high pressures, while the pump system must guarantee efficient and smooth operation.
Control Systems: Manual, Semi-Automatic, and Fully Automatic
Control systems vary across different types of hydraulic bending machines. Manual machines typically have basic control mechanisms, while semi-automatic and fully automatic machines feature more sophisticated controls. These systems can include programmable logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), and other digital interfaces that allow precise control over the bending process. Advanced control systems enhance operational efficiency and ensure consistent quality.
Supporting Structures: Frames and Dies
Supporting structures, including frames and dies, are critical to the machine’s function. The frame provides the necessary stability and support, ensuring that the machine can handle the pressure exerted during the bending process. Dies are used to shape the material as it is bent, and they must be designed to meet specific bend requirements. The quality and maintenance of these structures are vital to the machine’s longevity and performance.
The Operational Workflow of a Hydraulic Bending Machine
The operational workflow of a hydraulic bending machine starts with the preparation of the material, which is securely clamped into place. The operator or automated system then sets the desired bending parameters. Once the settings are confirmed, the hydraulic system is engaged, and the pump generates the necessary pressure to the cylinder. The cylinder pushes the material into the die, achieving the specified bend. Upon completion, the material is released, and the cycle repeats as needed. This process ensures accurate, repeatable bends with minimal human intervention.
Comparing Hydraulic Technology with Other Bending Technologies
.webp)
Differences Between Hydraulic and Mechanical Bending Machines
Hydraulic and mechanical bending machines have distinct operational principles and use cases. Hydraulic Bending Machines utilize fluid power to apply consistent pressure, enabling them to handle various material types and thicknesses with high precision. This technology ensures smooth and controlled bends, which is essential for intricate designs. On the other hand, mechanical bending machines rely on mechanical force generated through gears and levers. While these machines can be effective for simpler tasks, they often lack the versatility and precision that hydraulic machines offer. Additionally, mechanical bending machines are generally less adaptable to complex bending requirements and may experience inconsistencies in force application. Hydraulic bending machines work by utilizing fluid power to exert a consistent amount of pressure, allowing them to precisely manage different types of materials and varying thicknesses. This method guarantees smooth, controlled bends that are crucial for detailed designs. Conversely, mechanical bending machines operate using mechanical force produced by gears and levers. Although these machines can perform well for straightforward tasks, they frequently fall short in versatility and precision compared to hydraulic counterparts. Furthermore, mechanical bending machines tend to be less flexible in meeting complex bending needs and might show variations in force application. Hydraulic Bending Machines employ fluid power to apply steady pressure, making it possible for them to process a wide range of material types and thicknesses with exceptional accuracy. This technology is vital for creating smooth and controlled bends necessary for intricate designs. In contrast, mechanical bending machines depend on the mechanical force generated by gears and levers. While they can handle simpler tasks effectively, they usually do not match the versatility and precision provided by hydraulic machines. Moreover, mechanical bending machines are typically less suitable for complex bending requirements and can exhibit inconsistencies in applying force.
Efficiency of Hydraulic vs. Pneumatic Benders
Hydraulic Bending Machines are known for their efficiency, particularly when compared to pneumatic benders. Hydraulic machines operate through hydraulic fluid, which allows for greater force application and more precise control over the bending process. This results in higher accuracy and consistency, which is crucial in industries where quality cannot be compromised. Conversely, pneumatic benders use compressed air to generate force. While they can be faster in certain applications due to the quick response of pneumatic systems, they often fall short in delivering the same level of precision and control as hydraulic systems. Additionally, pneumatic machines may be less effective when dealing with thicker or more rigid materials.
Selecting the Right Hydraulic Bending Machine for Your Needs
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Machine
When selecting a Hydraulic Bending Machine, several factors need to be considered to ensure you choose the right equipment for your specific needs.
Material Type and Thickness
The type and thickness of the material you aim to bend significantly influence the choice of bending machine. Different machines are designed to handle various materials, ranging from thin sheets of metal to thicker, more robust materials. Knowing the specific requirements of your material will help you select a machine with the appropriate pressure capabilities and die configurations. Ensuring the machine can handle the thickness and type of material will prevent operational inefficiencies and potential damage to the machine or material.
Volume and Frequency of Operations
The volume and frequency of your bending operations are also critical factors to consider. For environments with high-volume production, a fully automatic Hydraulic Bending Machine might be the optimal choice due to its advanced features and efficiency. These machines are capable of handling continuous operations with minimal downtime, thereby enhancing productivity. On the other hand, for operations with lower volume and less frequency, a manual or semi-automatic machine may be adequate. These machines provide flexibility and are easier to manage for smaller-scale tasks, avoiding the higher costs associated with fully automated systems.
Evaluating Cost-Benefit Aspects
Cost-benefit analysis is a fundamental aspect of selecting the right Hydraulic Bending Machine. While upfront costs for hydraulic machines tend to be higher, the long-term benefits often justify the investment. These benefits include reduced labor costs, enhanced precision, and higher production efficiency. It is important to weigh the initial investment against the expected return in terms of productivity gains, reduced material wastage, and improved product quality. Additionally, consider the maintenance costs and the lifespan of the machine, as well-built hydraulic systems tend to require less maintenance and have longer operational lives, further adding to their cost-effectiveness.
Maintenance Tips for Prolonged Machine Life
Regular Inspection Routines
Regular inspection routines are essential for maintaining the optimal performance of a Hydraulic Bending Machine. Conducting frequent checks on key components such as the hydraulic cylinder, pump system, and control mechanisms ensures that potential issues are identified early. Routine inspections might include examining fluid levels, looking for any signs of wear and tear, and ensuring that all bolts and connections are securely tightened. By integrating these inspections into a scheduled maintenance plan, operators can prevent unexpected breakdowns and extend the machine’s operational lifespan.
Common Troubleshooting Techniques
Understanding common troubleshooting techniques can significantly reduce downtime and improve the efficiency of a Hydraulic Bending Machine. Operators should be familiar with the machine’s manual and its specific error codes, which can help diagnose issues quickly. Common problems might include hydraulic fluid leaks, unusual noises during operation, and difficulty achieving desired bends. Regularly checking for clogged filters and ensuring that the hydraulic fluid is clean and at the appropriate level can mitigate many issues. Troubleshooting should also involve inspecting the control systems to ensure that all digital interfaces are functioning correctly and that there are no software glitches.
Importance of Professional Servicing
While trained operators can manage routine maintenance and troubleshooting, the importance of professional servicing for a Hydraulic Bending Machine cannot be understated. Certified technicians possess the specialized knowledge required to conduct comprehensive inspections and repairs that surpass routine maintenance tasks. Professional servicing encompasses recalibrating control systems, replacing worn-out components, and updating software to the latest versions. By scheduling regular professional servicing, compliance with industry standards is maintained, machine performance and reliability are enhanced, productivity is increased, and long-term maintenance costs are reduced.
Future Trends in Hydraulic Bending Technology

Innovations in Automation and Robotics Integration
The future of Hydraulic Bending Machines lies in the integration of automation and robotics. Automation technologies are making these machines smarter and more efficient, with advancements such as real-time monitoring and adaptive control systems. By integrating robotics, manufacturers can achieve even higher levels of precision and speed. Robotic arms can be programmed to handle material feed, positioning, and removal, reducing the need for human intervention and minimizing errors. As a result, production lines become more efficient and capable of handling complex bending tasks with ease.
Sustainable Practices in Manufacturing
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in manufacturing, and Hydraulic Bending Machines are no exception. Future trends indicate a shift towards more environmentally friendly practices, such as using biodegradable hydraulic fluids and energy-efficient components. Manufacturers are also exploring ways to recycle waste materials produced during the bending process and minimize energy consumption through smart control systems. These sustainable practices not only reduce the environmental impact but also cut operating costs, making it a win-win situation for businesses. Emphasizing sustainability in the design and operation of hydraulic bending machines ensures that they align with global efforts to combat climate change and promote responsible manufacturing practices.
By addressing regular maintenance, adopting professional servicing, and staying abreast of future trends, businesses can maximize the efficiency and longevity of their Hydraulic Bending Machines while staying competitive in an ever-evolving industrial landscape.
XINBO is a company that prides itself on providing excellent custom services to its customers. With a team of professional engineers and designers, XINBO is able to quickly and accurately design detailed drawings according to the specific needs and requirements of its customers. This ensures that the final product matches the desired profile and specifications.
Related Posts

Good quality
XinBo machine making CO. LTD is a professional manufacturer and exporter in roll forming machine,
VIEW MORE→

 Spanish
Spanish Russia
Russia